1. User-server state : cookies
many Web sites use cookies four components:
1) cookie header line of HTTP response message
2) cookie header line in next HTTP request message
3) cookie file kept on user's host, managed by user's browser
4) back-end database at Web site
example :
- Susan always access Internet from PC
- visits specific e-commerce site for first time
- when initial HTTP requests arrives at site, site creates:
‣ unique ID
‣ entry in backend database for ID
what cookies can be used for :
- authorization
- shopping carts
- recommendations
- user session state (Web e-mail)
2. Web caches (proxy server)
• goal : satisfy client request without involving origin server
- user sets browser : Web accesses via cache
- browser sends all HTTP requests to cache
‣ object in cache : cache returns object
‣ else cache requests object from origin server, then returns object to client
More about Web caching
• cache acts as both client and server
• typically cache is installed by ISP(university, company..)
why Web caching?
• reduce response time for client request
• reduce traffic on an institution's access link
• Internet dense with caches : enable 'poor' content providers to effectively deliver content
3. Conditional GET
• Goal : don't send object if cache has up-to-date cached version
• cache : specify date of cached copy in HTTP request
• server : response contains no object if cached copy is up-to-date
4. Electronic mail
• User Agent
- composing, editing, reading mail messages
- e.g) Outlook, iPhone mail client
• Mail Servers
- outgoing, incoming messages stored on server
- mailbox contains incoming messages for user
- message queue of outgoing mail messages
• Mail Protocols
- simple mail transfer protocol(SMTP)
- POP3, IMAP, HTTP
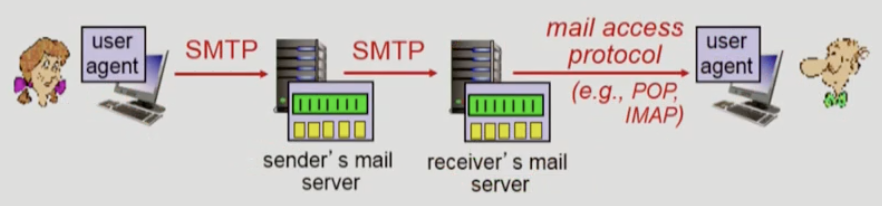
• SMTP protocol
- from user agent to mail server to send email message
- SMTP uses persistent connections
- uses TCP to reliably transfer email message from client to server, port 25
- command/response interaction
‣ commands : ASCII text
‣ response : status code and phrase
✓ comparison with HTTP:
- HTTP : pull, each object encapsulated in its own response msg
- SMTP : push, multiple objects sent in multipart msg
- both have ASCII command/response interaction, status codes
'네트워크 (이화여대 이미정)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Network Class 5 (0) | 2021.07.31 |
|---|---|
| Network Class 4 (0) | 2021.07.29 |
| Network Class 3 (0) | 2021.07.24 |
| Network class 2 (0) | 2021.07.23 |
| Network class 1 (0) | 2021.07.23 |



